To prevent exposing your sensitive data when sharing your code, environment variables are useful to save the data (either on your local machine or your production server) which your project depends on. In this article, we would learn how to use django-environ to create our environment variables for our Django project.
In our virtual environment, we enter the below to install the latest version of django-environ.
pip install django-environ
After installation, we use the pip freeze > requirement.txt to put the django-environ into the requirement.txt file.
Next, we would create a .env file in the folder containing our settings.py file.

In the .env file, we include the data we want to save such as our Django project SECRET_KEY
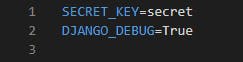
Ensure you add your .env file to your .gitignore file to prevent it from being committed to your version control system (such as GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket, etc.).
In our settings.py file, we include the following;
import environ
env = environ.Env()
environ.Env.read_env()
From the image above, we saved our SECRET_KEY and Debug boolean value in the .env file. To access them in our settings.py, we enter the following;
SECRET_KEY = env('SECRET_KEY')
...
DEBUG = eval(env('DJANGO_DEBUG'))
env('DJANGO_DEBUG') would give us a string value. To change the string to a boolean value, we use the eval function. We could add more data to our .env file and access them using the env function.